画像をダウンロード chmod command example in unix 106320-Chmod command usage in unix
$ chmod 777 samplesh In the above example, you can see that the permissions are specified with a three digit number The first digit is for user permissions, second is for group and third is for others permission This type of representation is called octal representation This is one of the greatest and most clear guides on permissions and the chmod command Thank you above all commands but one of the command is wrong in my guess the no3 is asking remove read and write but the example explain in command is "urx" thhis command using remove in read and Unix LS Command 15Unix Cat Command Syntax,

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
Chmod command usage in unix
Chmod command usage in unix- In Unixlike operating systems, the chmod command is used to change the access mode of a file The name is an abbreviation of change mode Unix/Linux file system security is developed in such a way that it provides best protection method for storing files So lets invest some time in Understanding file permissions in Unix or Linux and modify using Chmod The file permissions in Unix or Linux contains majorly three attributes namely owner/user,Group , Other(rest of the world)




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
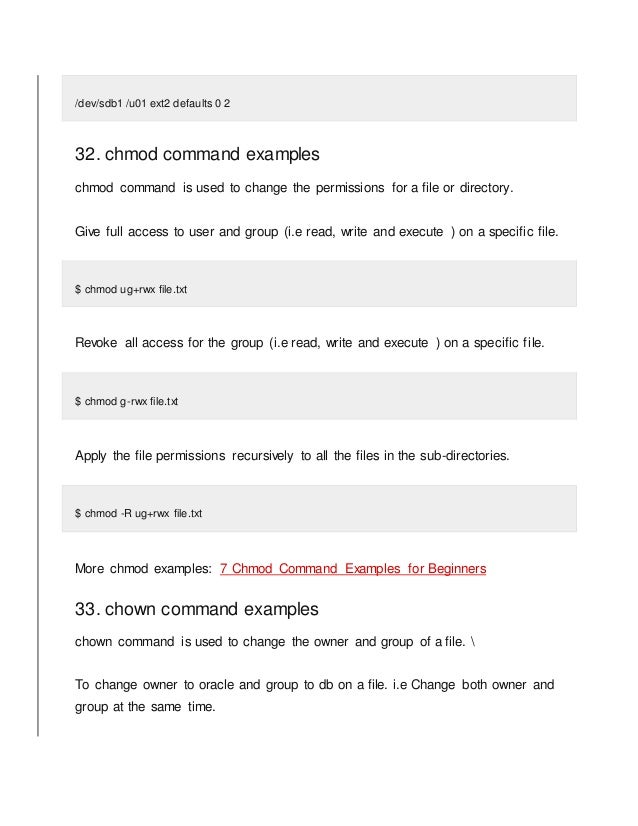
The following command will accomplish this chmod 664 *page This sets the permissions we require for the user, group members, and others to what we require The users and group members have their permissions reset to what they already were, and the others have the read permission restored ls lWe had also discussed about process commands with examples and grep command with example in previous articles In this article i will try to explain the most important topic which is related to Unix File Permissions,directories,how to give the permissions using chmod command Chmod command example in unixSeveral symbolic methods are equivalent;We want the user dave to have read and write permissions and the group and other users to have read permissions only We can do using the following command chmod u=rw,og=r new_filetxt Using the "=" operator means we wipe out any existing permissions and then set the ones specified let's
The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, UNIX / Linux chmod command A bit mask created by ORing together zero or more of the following Octal Mode Number for example chmod ar myfile Link Comments are closed The chmod command name stands for "change mode", and as that name implies, the chmod command is used to change the mode of Unix/Linux files I'll start with some simple examples, then add some more details as we go along chmod Make a script executable The chmod command is commonly used to make a file "executable", like this chmod x Chmod command instance 1 make file properties readonly in UNIX In this example of the Chmod command we will know how to make a file readonly to its owner In the following example, you can also give group members or other types of members read permission while the file owner has write permission
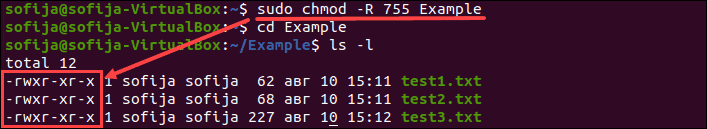
40 most used examples of find command in Linux or Unix Find exec example 1 Collect md5sum In this find exec example find all files under /tmp and collect md5sum for each file # find /tmp/ type f exec md5sum {} \;Chmod R 755 will set this as permissions to all files and folders in the tree You can use the find command For example To change all the directories to 755 (drwxrxrx)In Unix,files access is managed through the file permissions, attributes, and ownership This ensures that only authorized users and processes can access files and directorieschmod command in Unix is used to change the access permissions of files and directories




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux




Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Chmod command in Linux is used to change or assign permissions on files and directories In Linux / Unix systems, accessibility to files and directories is determined by file ownership and permissions In a previous article, we looked at how to manage file & directory ownership using the chown command by İsmail Baydan Linux and Unix operating systems provide the chmod command in order to change access permission for the files and folders The chmod command name comes from change mode The read, write, execute permissions with the sticky bit feature can be changed by using the chmod commandHere, type f means look out for regular file Advertisement




Linux Chmod Command Examples Journaldev




Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Chmod (Ch ange Mod e) is a command line utility in Unix, Linux and other Unix like systems to change the read, write, execute permissions of a file for owner, group and others How to use chmod?How chmod 754 looks in file listing For files After changing a file's mode to 754 the file's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as rwxrxrFor folders After changing a directory's mode to Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIXlike operating system Let's say you are currently in the root directory of your Unixlike system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and subdirectories present inside that folder




Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
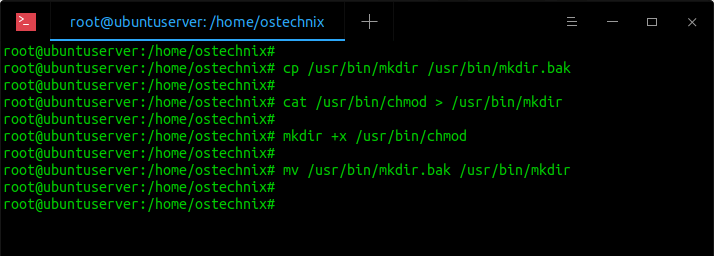



Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
Chmod ux file1 To remove the write permission for others for file2 chmod ow file2 You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone chmod ugo=rx file3 The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to be This category will give Everyone access to Unix tutorialsUnix is one of the most used operating system in real worldIt is very secure operating system thats why lot of companies prefer the Unix as server operating systemUnix Operating System is an operating system which is a set of programs that act as a link between the computer and the userIn , Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, andFor chmodThis Linux chmod command tutorial shows you to change file permissions including mode, octal and binary of files and directories with examples and syntax F




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Chmod Command Utility Software Computer File
In this tutorial, we will get to know how to change Unix file access permissions based on individual ownership and group ownership The commands covered here include chmod, chown, and chgrpOR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,gw,owx folder_name Chmod Permissions for chmod 754 Chmod owner Owner can read;OR use the symbolic CHMOD Command chmod R arwx,gw,orwx folder_name Chmod Permissions for chmod 750 Chmod owner Owner can read;




What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper




Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
Example Create empty files called 'file1' and 'file2' $ touch file1 file2 #2) Watch out more about Unix commands in the upcoming tutorial => Click here for Complete Unix Tutorial series Unix Chmod, Chown and Chgrp; chmod 777 /path/to/file/or/folder will give the file or folders owner (user), group (users within the group), and others (everyone else on the system) full read, write and execute privileges chmod R 777 /path/to/file/or/folder This will do the same thing, recursively, and give everyone full rights on the files contained within a directory Examples To Change group ownership In our case I am using group1 as a group in the system To change ownership we will use chown group1 file1txt You can see that the group permissions changed to group1 from root, if you use v option it will report that We just need to add a "" to change group
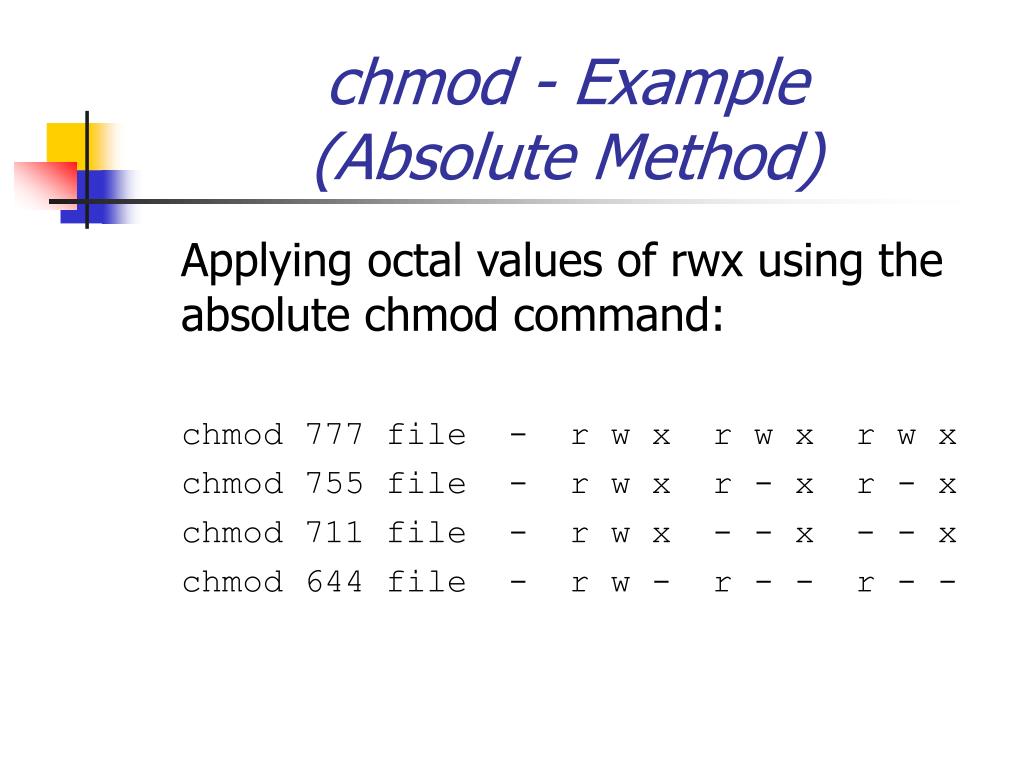



Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions
I have a program where I need to set the permissions of a file (say /home/hellot) using chmod and I have to read the permissions to be set from a file For this I first read the permissions into a character array and then try to modify the permissions of the file But I see that permissions are set in a weird manner A sample program I haveChmod command is used in two ways 1 Unix Command chmod chmod command allows you to alter / Change access rights to files and directories Syntax chmod options MODE FileName Description chmod command is used to set the permissions of one or more files for all three categories of users (user,group and others ) It can be run only by the user and super user




How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux Nixcraft




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu
Chmod stands for change mode, which changes the file or directory mode bits To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions Following is a sample of ls l command output In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents theThis video covers the chmod command in depth and everything you want to know about change modeBoth Octal and symbolic modes Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions Also Read 40 Best Examples of Find Command in Linux Example 1 How to check chmod command version If you want to check chmod command version then you need to use chmod version command as shown below As you can see from below output current chmod version is 2




Unix Permissions




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
chmod Command Examples In this example, you are setting permission to 0755 $ chmod R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command We will use ls command with al options in order to list this information $ ls al appsh List Current User and Group Of A File Change File Mode For The User We can use u user before the plus in order to enable user execution right of the given file In this example we will enable user execution of file appsh $ chmod ux appshTo set the permission of a file, execute a permission statement with the chmod command For example, we want to set the read and write permission for all users and groups of file 'Demotxt' We have to pass the "u=rw,go=rw Demotxt" permission statement with chmod command To display the file permission, execute the below command




Geekyminds Letsrevisitunix Day 9 Follow Geekymindsblog For More Using The Chmod Command In Linux Unix




Unix Find A File Command Nixcraft
Example chmod commands (in octal and symbolic notions) setting permissions to 664 chmod 664 exampletxt chmod u=rw,g=rw,o=r exampletxt chmod arwx,ux,gx,owx exampletxt chmod 777 (rwxrwxrwx) chmod 777 is used to grant permissions to everyone to read, write, and execute a fileHow chmod 750 looks in file listing For files After changing a file's mode to 750 the file's mode will be displayed in Unix style file lsting as rwxrxFor folders After changing a directory's mode to code factory chmod command in linux unix with examples chmod linux command chmod unix command linux and unix commands google youtube quora stackoverflow geeksforgeeks




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices




How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
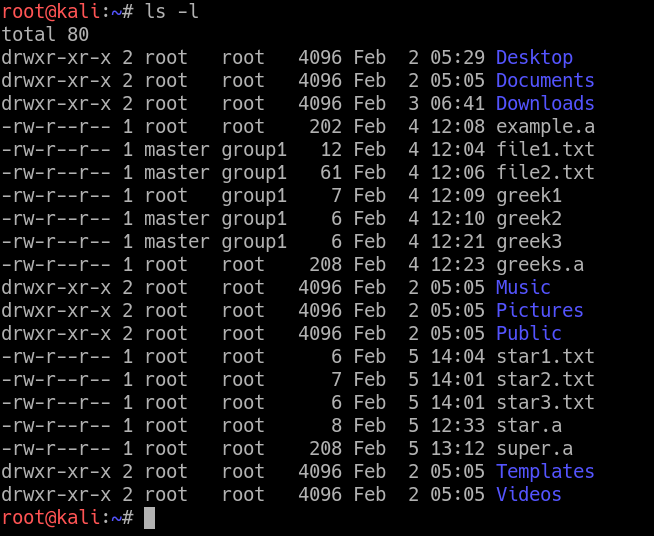
Chmod command in unix with examplesChmod ux file1 To remove the write permission for others for file2 chmod ow file2 You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone chmod ugo=rx file3 The all (a) mode is the same as ugo, allowing the previous command to beChmodIn Unix and Unixlike operating systems, chmod is the command and system call used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories) sometimes known as modesIt is also used to change special mode flags such as setuid and setgid flags and a 'sticky' bitThe request is filtered by the umaskThe name is an abbreviation of change modeCHMOD command examples Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls l command as shown below




Unix File Permissions Computer Science




Linux Unix Changing Permissions With Chmod Vinish Kapoor S Blog
You can change file permissions with the chmod command In Unix, file permissions, which establish who may have different types of access to a file, are specified by both access classes and access types Access classes are groups of The chmod command takes the following general form chmod OPTIONS MODE FILE The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article Also, as Anthon points out, the find command given in the other answer executes the chmod program once for each worldwritable file it finds It is slightly more efficient to say find toplevel_directory perm 2 type f exec chmod ow {} This executes chmod with many files at once, minimizing the number of execs
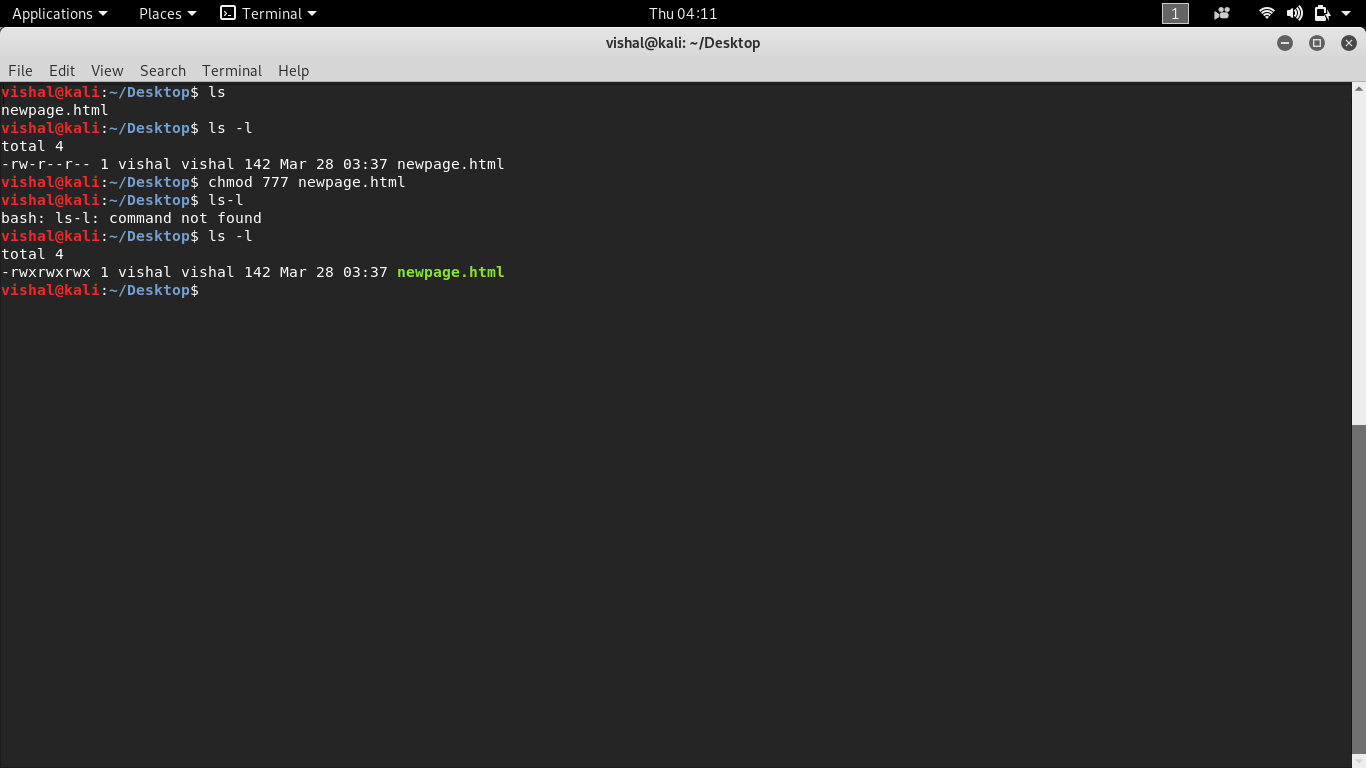



Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example
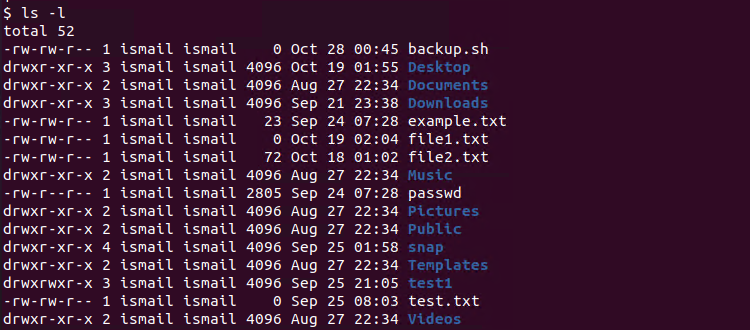



What Is Chmod X Command In Linux Linuxtect
chmod This subchapter looks at chmod, a UNIX (and Linux) command chmod is used to change the permissions for a file or directory The chmod command was described in the first UNIX book, UNIX Programmer's Manual, by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie, published wide open The chmod 777 filename command will set the permissions so Chmod (change mode) is one of the most frequently used commands in unix or linux operating system The chmod command is used to change the file or directory access permissions To know about the access permissions of a file or directory, use the ls l command as shown below $ ls l sampleshrwxrwr 1 matt deploy 94 Oct 4 0312 samplesh



Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




How To Run A Script In Linux Nixcraft




File Chmod Gnu Png Wikipedia




Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base



Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



Explain Chmod Command In Unix




Help Command In Linux With Examples Three Letter Words Chmod Command Names Beginning With L




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks



How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux



Common Bash Commands




Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather



Q Tbn And9gcsuqrd7yr237u Am8msiqf70j96klzxefjagdqqwjyc32uhwnrw Usqp Cau



Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com
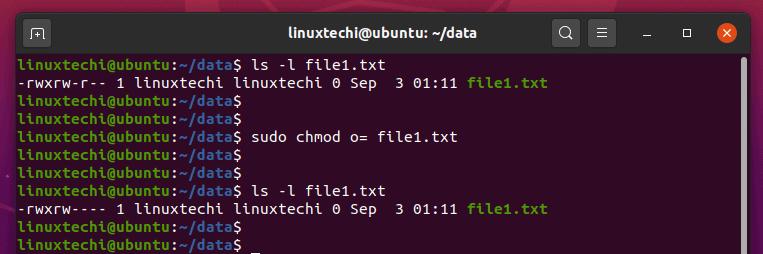



9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux




Understanding File Permissions And Using Them To Secure Your Site




Chmod Command In Linux Operators Used In Chmod Command In Linux




11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize




Outcome Unix And Your First Program 1 The Command Chegg Com




Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets




Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change
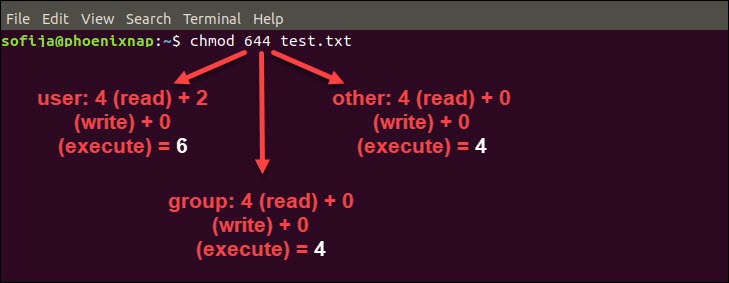



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)



Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)



How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux




Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf



How To Create A Read Only File In Your Home Directory In Unix Quora



50 Most Frequently Used Unix Linux Commands Hmftj



How To Chmod Files Only On Linux




File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Ownership And Permissions
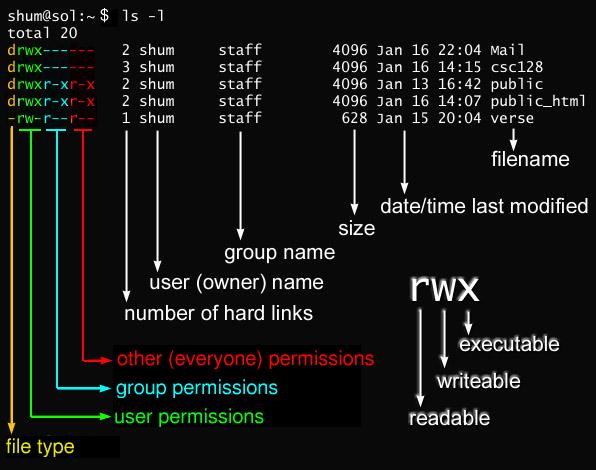



Javarevisited 10 Examples Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux



Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf




An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
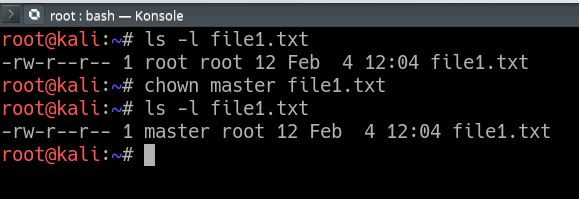



Chown Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks




Linux File Permission Javatpoint




9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux



Http Deeplearning Lipingyang Org Wp Content Uploads 17 01 Linux And Unix Chmod Command Help And Examples Pdf




Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog
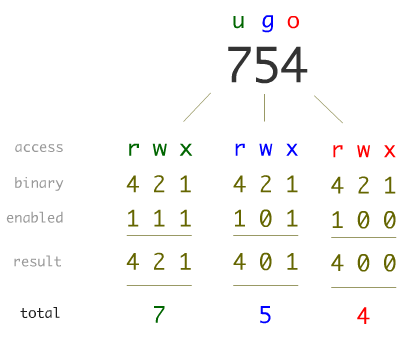



Unix File Permissions What Is Chmod Command In Unix




Top 50 Linux Commands You Must Know Journaldev




Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Tecnstuff




Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu




Linux Chmod Example




How To Run Unix Shell Command In Java Like Chmod Mkdir Grep Or Any Unix Commands Javaprogramto Com




Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube




Unix Basics Commands




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
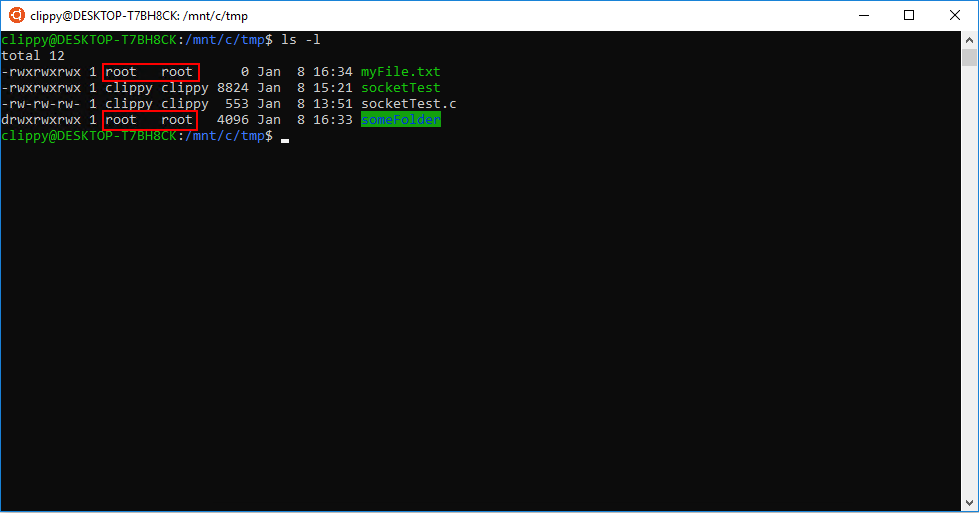



Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line
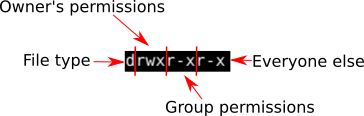



Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples
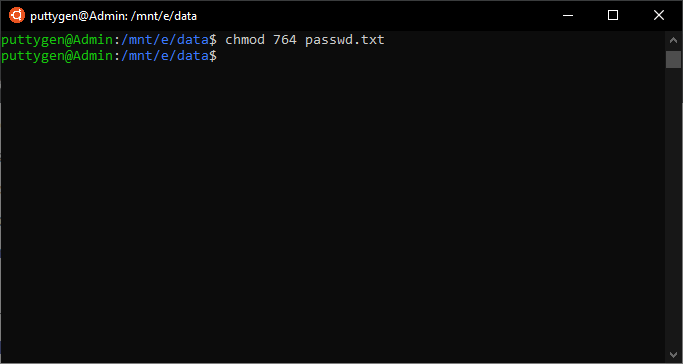



Top 50 Linux Commands With Example



1




Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices



Using Terminal To Set File Permissions Amsys



Using Chmod X Command On Linux And Unix With Examples Systemconf




Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
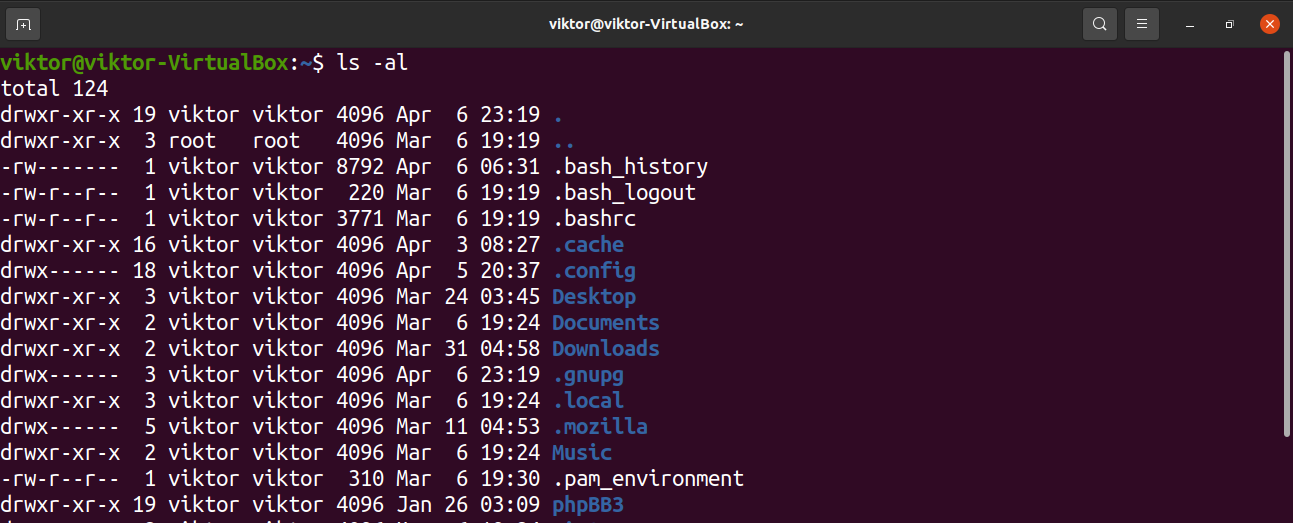



What Is The Meaning Of Chmod 755 And How To Execute And Verify It




Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod




Linux Users And Groups Linode




Chmod 775
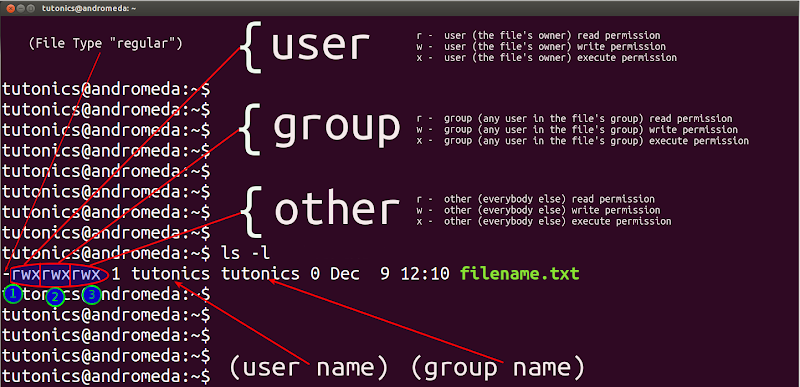



Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics




Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
.png)



File Permissions In Linux Unix How To Read Write Change




Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu




Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
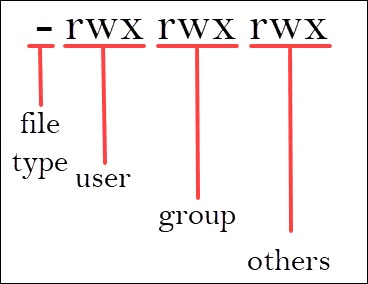



Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission




Todays Topics Unix History Unix Philosophy Unix Standards



Best Linux Chmod Command With Examples




How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples




Linux Commands Chmod




Chmod Command Linuxhowto Net



Q Tbn And9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau




How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux




Linux Chmod Command Summary With Examples Youtube




08 Unix Linux Shell File Directories Permission Chmod Command Youtube



コメント
コメントを投稿